Osteochondrosis is a disease with a wide distribution, at the age of 35-40 it is found in varying degrees in most people. The most likely localization of osteochondrosis is the lower cervical, upper thoracic and lower lumbar spine. The etiology of osteochondrosis, that is, the specific causes and conditions of onset, is completely unknown. However, there is a direct influence of hereditary predisposition, age-related changes, injuries and weakening of the blood supply to the tissues.
In the development of the disease, the main role is played by changes in the central part of the intervertebral disc, namely dehydration. Recall that the disc is made up of the nucleus pulposus and the fibrous ring that surrounds it. Due to drying, the disc loses its shock absorbing functions, which leads to gradual destruction. In the development of the disease, four stages are distinguished, which differ in some changes in the disc and adjacent tissues. The severity of osteochondrosis of the spine, symptoms and treatment directly depend on the stage of development of the pathology.

Symptoms and causes of osteochondrosis of the spine
Let's briefly consider the stages of the progression of osteochondrosis in terms of anatomical changes.
- First stage. The formation of cracks in the inner layers of the fibrous ring and in the nucleus pulposus. Penetrating into the cracks, the nucleus irritates the nerve endings of the fibrous ring;
- Second phase. While further irritation of the fibrous ring occurs due to the pathology of the nucleus pulposus, the fixation of the vertebrae deteriorates. There is unusual mobility of the spine;
- Third stage. Gradual damage to the annulus fibrosus. There is a protrusion of the nucleus (protrusion) beyond the anatomical boundaries of the fibrous ring, then a rupture of the ring occurs and the formation of an intervertebral hernia (extrusion);
- Fourth stage. There is a spread of degenerative changes in the surrounding tissues: vertebrae, ligaments, nerves, blood vessels. Due to chronic inflammation, the intervertebral disc is scarred, which leads to the development of fibrosis.
Depending on the location in the spine, there are 3 types of osteochondrosis:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- Thoracic osteochondrosis;
- Lumbar osteochondrosis.
It is worth noting that some sources distinguish the fourth type - sacral osteochondrosis.

Cervical osteochondrosis |
Thoracic osteochondrosis |
Lumbar osteochondrosis |
|---|---|---|
|
The main types of osteochondrosis are considered to be cervical and lumbar. However, the thoracic spine is constantly under stress and is prone to the early development of major degenerative changes, especially in young people. Due to the peculiarities of the development of changes in the thoracic spine, neurological symptoms manifest themselves at an advanced stage of the disease. In most cases, the disease occurs with an injury (for example, due to lifting too much weight).
|
Abnormalities are most often observed in the lumbar spine.
|

It was previously said that the etiology of osteochondrosis is not fully understood. However, we can name the main causes of osteochondrosis of the spine, with a proven effect on the development of the disease:
- Regular static and dynamic loads on the spine of varying intensity. For example, the work of a loader (carrying weights) or a miner (staying in unnatural positions for hours and a huge physical load), a driver (vibrations and a sedentary lifestyle) or an employee (a sedentary lifestyle ;
- back injury;
- Weak or overweight physical development;
- Failure to maintain correct posture and stoop
- Flat feet and muscle imbalance as a result lead to an uneven distribution of the load on different parts of the spinal column;
- genetic characteristics;
- Hypothermia leads to more intense symptoms of osteochondrosis;
- And finally, the human aging process.
Spine Osteochondrosis Diagnosis
Preliminary diagnosis of the disease (osteochondrosis) occurs on the basis of the patient's complaints, his examination and palpation of the spine. In addition, the affected part of the spine can be identified thanks to the topography of pain spread, which is able to tell exactly where (in the vertebrae of the neck, chest, lower back) the compression of the nerves has occurred.
The main diagnostic method for diagnosing osteochondrosis is an X-ray examination. On the x-ray of the spine, degenerative changes in the intervertebral joints, discs, narrowing of the intervertebral canal, sclerotic changes in the tissues of the spine are noted. At the same time, the recognition of spinal injuries (especially at the early stage) is always difficult, since the processes occurring in this case are characteristic of numerous other diseases (tumors, metastases, ankylosing spondylitis, tuberculous lesions).
On the frontal radiographic images, the irregularity of the plates, an increase or a refinement of the uncinate processes are detected. In the profile pictures, a decrease in height, a change in shape, a herniated disc, osteophytes and other changes in the vertebral body are noted. Small degenerative changes are not visible on a simple X-ray, and an X-ray examination using contrast is performed to detect them. The most complete information can be provided by the discography - an X-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent through a puncture directly into the intervertebral disc.
Another study of the spine is a functional X-ray method. Thanks to radiography performed with maximum flexion and extension of the spine, it is possible to determine the mobility or immobility of the intervertebral space.
The most modern and high-tech research methods are computed tomography (hereinafter referred to as CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (hereinafter referred to as MRI). Although the first CT and MRI machines appeared in the 1970s and 1980s, the technologies are still actively developed and improved, while remaining quite inaccessible to the general population due to the high cost of examinations or the lack of machines in hospitals. locals.
Methods of treatment of osteochondrosis of the spine
Treatment of osteochondrosis is a long periodic complex process. It is aimed at reducing and eliminating the consequences of changes in the intervertebral disc. Namely, inflammation, squeezing, poor blood flow, muscle spasms. Many types of therapy can help in this process, including the methods of Eastern healers. In the treatment of osteochondrosis, the patient needs complete rest.
For the most part, treatment is done with non-invasive methods, such as drug therapy, anti-parasite therapy, physical therapy, and others. Invasive therapy, ie surgical operations, is rarely used. For example, in such cases where the intervertebral hernia persists for more than six months and conservative treatment does not give a positive effect.

Osteochondrosis of the spine and its treatment are carried out by doctors of various specialties: neurologist, orthopedist, vertebrologist, chiropractor and others. However, the diagnosis, the appointment of tests and studies, is usually carried out by a neurologist and a vertebrologist, if a doctor of this specialty is available in the clinic, due to his specialization in diseases of the spine.
Summing up, we can say that the treatment of osteochondrosis is divided into the following main categories:
- Reduction of pain syndrome;
- Removal of spasms;
- Elimination of inflammation;
- Reduction of squeezing;
- Improvement of blood flow;
- Prevention of further deterioration.
Let's take a look at commonly used treatments, each of which covers one or more items on this list.
Physiotherapy treatment
Physiotherapy procedures are aimed at improving blood microcirculation in the area of the affected spine, eliminating pain and relieving edema. In addition, physiotherapy helps reduce the doses of the drugs used. There are dozens of types of physiotherapy. Here are a few:
- Reflexology is the impact on acupuncture points with needles, electricity, laser. Helps relieve spasm and improve blood flow;
- Kinesiotherapy is a treatment through movement and special physical exercises. Indeed, this is therapeutic gymnastics, but in a broad sense. This includes training on simulators, group exercises under the guidance of a doctor, stretching the spine;
- Therapeutic swimming. It allows you to perform exercises with damage to the spine for those patients who have difficulty performing them. For example, the elderly, people who are overweight or with walking disabilities. It is important to note that due to the lifting force of the water, there is an even distribution of loads on the spine;
- Impulsive current therapy, UHF therapy, neurostimulation, magnetotherapy, massage and more.
Acupuncture
A unique method that came from oriental medicine. Its essence lies in the use of very fine special needles that enter special points of the body, literally, under the influence of gravity. These points were discovered by thousands of years of experience of oriental healers, then proven by mainstream medicine. Acupuncture also helps to eliminate excruciating pain, has a positive effect on the nervous system as a whole and on nervous diseases.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is indicated only if there is no positive effect from non-invasive treatment or in case of serious complications. The main method of surgical treatment is discectomy - the removal of a damaged disc. However, even after the operation with minimally invasive methods, rehabilitation will take at least 6 months.
At the same time, surgery will not eliminate the need for regular osteochondrosis treatment. Since before the operation there is always a clear task to eliminate a specific defect: hernia, deformity, subluxation, etc. The operation does not affect the general degeneration process of the cartilage tissue of the spine.
Medical treatment
This type of treatment is most effective in the short term. Medicines immediately reduce pain, eliminate inflammation, relieve spasms, etc. However, as soon as they are canceled, in the absence of other necessary procedures for the treatment of osteochondrosis, their effect quickly disappears. At the same time, you can not spend your entire life on drugs, sooner or later they will have a side effect on the body.

Drugs can be classified as both primary and secondary treatment. They are often needed to improve the patient's life. They are used to relieve pain (therapeutic block), eliminate inflammation, relieve muscle spasms, improve blood flow. In recent years, another type of medicine is increasingly used: chondroprotectors. However, drugs alone cannot achieve a long-term permanent effect.
Treatment at home
Home treatment of osteochondrosis consists of manual therapy (physical therapy, Shants collar), acupuncture and vacuum therapy. These methods help improve blood circulation and reduce congestion in the muscles and spine. As a result, tissue regeneration is significantly improved.
The listed procedures in combination with drugs provide effective treatment that relieves unpleasant symptoms and improves the general condition. In this case, special attention should be paid to proper nutrition and regulation of excess weight.
Physiotherapy
Thanks to gymnastics, the mobility of the vertebrae is restored, the muscles and their circulatory system are strengthened. The latter is of great importance, because the spine is deprived of its blood supply system, and the intervertebral disc can receive nutrients only through adjacent tissues. In this case it is necessary to distinguish between therapeutic exercises and any other training.
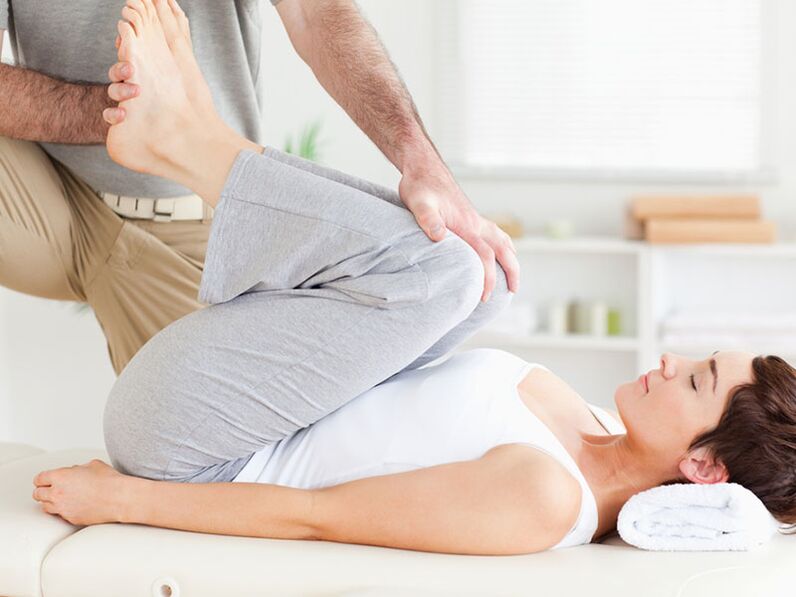

Manual therapy
One of the most effective methods. Since the manual therapist affects the muscles, ligaments and bones. It improves posture, restores the "normal" structure of the skeleton, relieves excess muscle tension. Including, it directly affects the vertebrae.
Manual therapy of osteochondrosis should be done regularly, from once a year to several times, as needed. It should be noted that this is not a one-time, multi-dimensional, 10-20 session procedure. Only then will it have a long-term positive effect.